Reasons Why the Engine Light is On
In general, the engine light can illuminate due to a fault with the vehicle’s engine, transmission or the Emission Control System. However, the reason for the engine warning light coming on varies depending on the vehicle, as some vehicles monitor more functions than others. Some of the common reasons why the engine light comes on include:
The job of the mass airflow sensor is to measure the quality of the oxygen coming into the engine. The mass airflow sensor generally lasts between 10,000 to 12,000 miles, though good routine maintenance and air filter replacement can extend its life. Symptoms of a failing mass airflow sensor include rough idling, engine is slow to react and engine stalls. If your mass airflow sensor is failing, the risk to engine damage is low.
The oxygen sensors measure the quantity of oxygen in the exhaust gasses that exit the engine. The sensors send data to the car’s computer to determine the correct air-to-fuel ratio for the car’s engine. Symptoms of failing oxygen sensors include reduced fuel economy, rough idling engine, loss of engine power and of course the check engine warning light will be illuminated. Depending on your car, it may have one, two, or more oxygen sensors and in general, they last upwards of 50,000 miles. Proper and regular maintenance helps to increase the lifespan of your vehicle’s oxygen sensors. If your oxygen sensors are failing, the risk to engine damage is low.
The EGR system is responsible for returning around 15% of exhaust gasses back into the engine’s combustion chambers where it’s burned. This essentially lowers combustion temperatures and helps to reduce toxic exhaust emissions. Symptoms of a failing EGR valve include rough engine idle, poor engine performance, poor fuel economy, engine stalling while idling, fuel odour and the engine warning light. The average lifespan of the EGR valve is around 10 years, so older vehicles may require an EGR valve replacement.
A diesel particulate filter (DPF) is an exhaust aftertreatment device that helps to prevent harmful diesel particulate matter from exiting the exhaust by trapping it in a filter. Over time, the filter becomes full and requires cleaning. This process is called regeneration and is often carried out automatically and passively without driver knowledge.
Integrated into a vehicle’s exhaust system is the catalytic converter. The job of a catalytic converter is to turn the carbon monoxide gas which is generated by combustion into the less harmful carbon dioxide. In general, a catalytic converter should last the lifespan of the vehicle, though this does depend on how well the vehicle has been maintained over the years. Symptoms of a failing catalytic converter can include poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, possible rattling sound, rotten eggs / sulphur smell and discoloured smoke from the exhaust and the engine warning light. A bad catalytic converter can potentially damage the engine. If the engine warning light is flashing, it can be a symptom of engine misfire and this can cause catastrophic heat in the catalytic converter.
Diesel and petrol cars have fuel filters and these are responsible for filtering contaminants from the fuel before the fuel enters the engine. Improper car maintenance or a faulty fuel filter may not properly filter contaminants prior to entering the engine and among other things, can result in blocked fuel injectors. How often the fuel filter requires changing depends on the vehicle. Older vehicles may require a filter change from between 20,000 – 30,000 miles and newer vehicles can have filters that last up to 60,000. Symptoms of blocked fuel injectors can include problems starting the engine, erratic engine performance, engine misfire, rough idling and the engine warning light. Continued driving with blocked fuel injectors will eventually result in vehicle breakdown and engine damage.
Spark plugs make up part of a petrol engine’s ignition system and if they haven’t been replaced in a while, it can cause the engine warning light to come on. Changing the spark plugs and spark plug leads is usually a good place to start if your vehicle is ageing and the engine light is on. While you’re at it, change the ignition coils too.
The engine warning light can often come on along with additional warning lights. Often the fault that causes the engine warning light to illuminate can cause another vehicle system to fail or to become intentionally deactivated and once the primary fault is rectified, the other warning lights may go off.
Along with the warning lights, other symptoms may occur such as reduced engine power. This is an intentional reduction in engine power to reduce the chances of engine damage.
Those are just some of the more common reasons for the engine warning light to come on, but due to the engine warning light being generic, it can illuminate on for a multitude of reasons and as such, you’ll either need to purchase diagnostic scanner tool to read fault codes and diagnose the engine light yourself, or take your car to a vehicle repair shop.
Diagnosing the Engine Warning Light
Unless you have a very old car, then it’s going to have something called an on-board diagnostics system – abbreviated to OBD. A newer, more sophisticated OBD called OBD II was developed and integrated into all cars manufactured in the US from 1996.
EOBD, the European version of OBD became a mandatory component of all petrol vehicles manufactured in the European Union from 2001 and for diesel vehicles from 2003.
Essentially, the OBD II is a computer which collects information via a network of sensors throughout the vehicle. OBD II regulates or monitors vehicle systems and alerts the driver of faults via dashboard warning lights or messages. In addition to warning lights and messages, fault codes are stored.
Diagnostic equipment called a OBD II scanner can be used to connect to the vehicle’s OBD II either wirelessly or via a physical port to read these fault codes.
The amount of information provided depends on the vehicle and on the scanner equipment used. From an OBD II scanner, you’ll be able to obtain information from the vehicle’s powertrain (engine and transmission) and the Emission Control Systems such as, but not limited to:
- Fault codes / Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Throttle / brake position
- Air / fuel ratio
- ABS fault diagnosis
- Airbag fault diagnosis and reset
- Catalytic converter temperature
- Exhaust CO2
- Engine coolant temperature
- Engine oil temperature
- Engine RPM
- Fuel flow rate
- Fuel level
- Exhaust temperature
- Fuel pressure
- Air flow rate
- O2 sensor test
- Steering angle sensor calibration
- Oil light / service reset
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Status of ‘Check Engine’ / engine warning light
- Ignition counter / cycles
- Full ECU diagnosis
One of the benefits of OBD II over the original on-board diagnostics systems is that they can monitor the gradual deterioration of a system and alert the driver via the engine warning light before complete failure of the system.
If you have knowledge on vehicle mechanics / electrics, owning your own diagnostic code reader / scanner is a valuable tool to have. When considering purchasing an OBD II diagnostic code reader, ensure that the model has high vehicle compatibility and in particular, compatibility with your vehicle. The type of OBD II scanner that you can purchase are:
1. Laptop based OBD II scanners
These OBD II scanner are cheap and draw power from the PC to operate. Essentially these are connecting devices between your laptop USB port and OBD II port in your car. You then use diagnostic software on your PC.
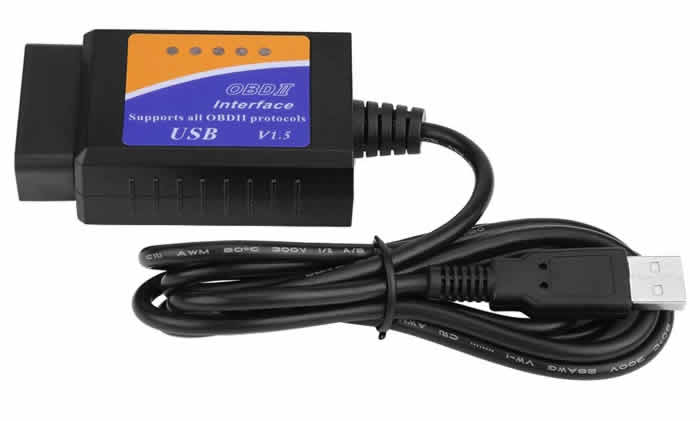

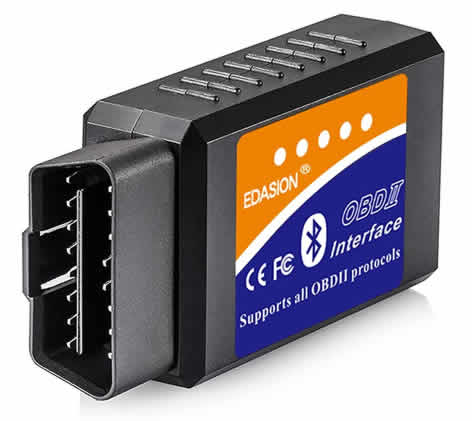
2. OBD II Bluetooth scanners
These OBD II scanners connect to your smart phone, tablet or laptop via Bluetooth. You then simply download the applicable app and install. Free and paid apps are available.

3. Handheld OBD II scanners
The handheld OBD II scanners are typically more advanced and have their own screen, interface, battery pack and cables. This is often the choice for the professional who intends to diagnose faults with engine, transmission, brakes, ABS, airbag, emission system etc. The handheld diagnostic fault code readers are often more expensive and range in price significantly.

Engine Fault Codes
The engine warning light, otherwise known as the check engine light or malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminates when a fault code has been logged. These codes can be read when a diagnostic scanner / fault code reader is hooked up to the vehicle’s OBD port.
Engine fault codes, or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) as they’re professionally known are 5 digit codes that identify a specific fault in the car. The codes are usually comprised of one letter followed by 4 numbers and some codes are specific to car manufacturer, while other codes are generic and used by all car manufacturers.
What to do if the Engine Light Comes On
You can often continue driving with the engine warning light on due to the system usually triggering the warning at the early stages of the fault. However, you should have your vehicle looked at as soon as possible before system failure, as this may cause further damage and result in higher costs.
Without a diagnostic fault code reader, you’re not likely to know why the engine warning light has come on. The engine warning light will either come on steady, or flash.
If the engine warning light comes on steady:
- Avoid hard acceleration
- Avoid high speeds
- Avoid towing heavy loads
- Have your vehicle booking in and repaired as soon as possible
If the engine warning light is flashing:
- Immediately reduce speed
- Avoid hard acceleration or braking
- If the engine warning light continues to flash, have the vehicle repaired immediately
A flashing engine warning light is more serious as it can indicate an engine misfire. This can result in damage to the vehicle’s emissions control system.
How to Turn Off the Engine Warning Light
Most fault code readers will provide the option to turn off or reset the engine warning light. However, simply resetting or turning off the engine warning light does not fix the fault and in many cases, the warning light come back on later.
Hi molefe if I first started my Toyota Hilux for first time to heat up engine not engine diagnosis sign if I park after a journey starting again it’s appearing turning engine off starting again it’s not longer appearing your advice
Hi Molefe,
It means you have an intermittent fault. When the engine light comes, fault codes are usually stored, so you’ll need to have these read by an OBD2 scanner. Get the codes read at an auto store. Just in case the codes are not being stored and no codes are readable, you might then benefit by purchasing your own scanner tool to hook up to the vehicle when the engine light comes on.
Hi There,
The engine warning light comes on steadily in my car when I checked with the Hyundai service centre. They are also not able to detect any fault currently. Is it safe for my car?
Hi,
It’s not particularly helpful when the engine light is on and no fault codes are stored. Generally it’s safe to continue driving. You’ll normally begin to see slight changes in your vehicle’s performance and how the engine runs, rather than just a breakdown. If you notice any differences, best to get it checked again. If you wish, you can also purchase your own diagnostic tools that plug into the OBD2 port and check for fault codes yourself.
2015 Chevy traverse with 76,000 check engine light on sensor says EVap anyone know what that is as I heard could b multiple things also just when I put gas in it does not wanna start it does that only when I put gas in after it starts it’s good oh n had a message on dash that said something about stabilizer unit ( did I get a lemon as I’ve only had car a year n had issues right when I got it n dealership refused to trade me out as I gave a hefty down deposit
Hi LeeAnn,
These EVAP issues are quite common with the Chevy. Basically the vehicle has a evaporation emissions system that stops vapor from going into the atmosphere and instead is sent back into the engine where it gets burned off. If there’s a problem with the system, you get the EVAP light and the engine warning light will also come on. It can be something as simple as your gas cap. If it’s loose or damaged and needs replacing. Take a look at your gas cap, ensure the seal is clean.
If you need to get another one, ensure it’s OEM as aftermarket caps might not work correctly and cause you errors again. If not, it may be a problem with the system itself. A common issue is the purge valve in the evap system. They’re usually quite easy to replace. You’ll need to have diagnostic (OBD-II diagnostic tool) to scan for the specific fault code so you know where the problem is. You can get diagnostics done for free at a lot of places. Once you have the trouble code, you’ll know what needs to be done.